Introduction : Dental Implant Anatomy
Understanding dental implant anatomy is crucial for both students preparing for exams and professionals working in clinical practice. Unlike natural teeth, implants have unique anatomical considerations that directly affect surgical planning, osseointegration, and long-term success rates.
In this article, we’ll cover the basics of dental implant anatomy, why it matters, and the best resources to master it—including modern digital study tools designed for exam prep and clinical application.
What Is Dental Implant Anatomy?
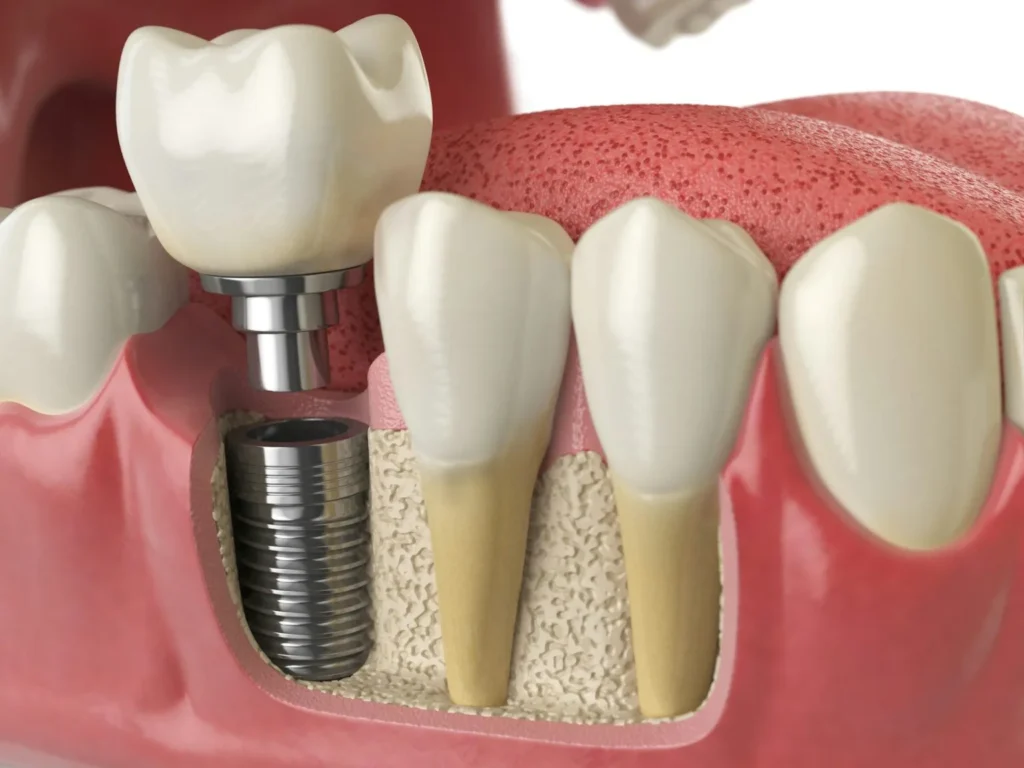
Dental implant anatomy refers to the structural and biological features involved in placing and maintaining a dental implant. Key components include:
Implant Fixture (Body): The titanium or zirconia screw inserted into bone.
Abutment: Connects the implant fixture to the prosthetic crown.
Crown/Prosthesis: The visible replacement tooth.
Surrounding Tissues: Alveolar bone, peri-implant mucosa, and gingiva.
A deep understanding of these structures is essential for avoiding complications and ensuring predictable results.
In this article, we’ll cover the basics of dental implant anatomy, why it matters, and the best resources to master it—including modern digital study tools designed for exam prep and clinical application.
Why Dental Implant Anatomy Matters
For students and professionals, mastering dental implant anatomy helps:
Improve surgical planning and placement accuracy
Prevent nerve injury, sinus perforation, and bone loss
Strengthen knowledge for exams such as INBDE, ADC, ORE, and NBDE
Bridge the gap between theory and real-life patient care
Core Principles of Dental Implant Anatomy
Here are the key areas every student should focus on:
Bone Anatomy
Density and volume of the alveolar ridge
Proximity to critical structures (sinus cavity, mandibular canal)
Soft Tissue Considerations
Keratinized gingiva vs non-keratinized tissue
Biological width around implants
Implant Positioning
Mesiodistal and buccolingual placement
Importance of emergence profile
Osseointegration
How bone cells interact with the implant surface
Key factor for implant stability and success
Best Resources for Learning Dental Implant Anatomy
If you’re searching for the right way to master dental implant anatomy, consider these options:
Textbooks – Contemporary Implant Dentistry (Misch), Dental Implant Prosthetics, and Clinical Periodontology and Implant Dentistry.
3D Models & Atlases – Visualizing implant positioning in relation to bone and nerves.
Digital Bundles (like the Dental Study Bundle) – All-in-one solutions with anatomy notes, implant case studies, and exam-style Q&As.
Why Students Prefer the Dental Study Bundle
Instead of juggling multiple books and PDFs, many students now turn to comprehensive digital resources like the Dental Study Bundle.
Here’s why:
✅ Covers dental implant anatomy in depth with diagrams and clinical applications
✅ Includes 380+ real clinical cases (implant placement, complications, treatment planning)
✅ 300+ Pages of Comprehensive Dental Notes
✅ Saves time with a digital planner and organized notes and more .
📘 Want a complete resource for dental implant anatomy and beyond?
➡️ Get the Dental Study Bundle now – 80% OFF today
